This post is also available in:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Nematodirus control
Solution name: Nematodirus control – forecast and anthelmintic use
Aim: To outline the effect of Nematodirus and why to treat with white drenches (benzimidazole)
Description:
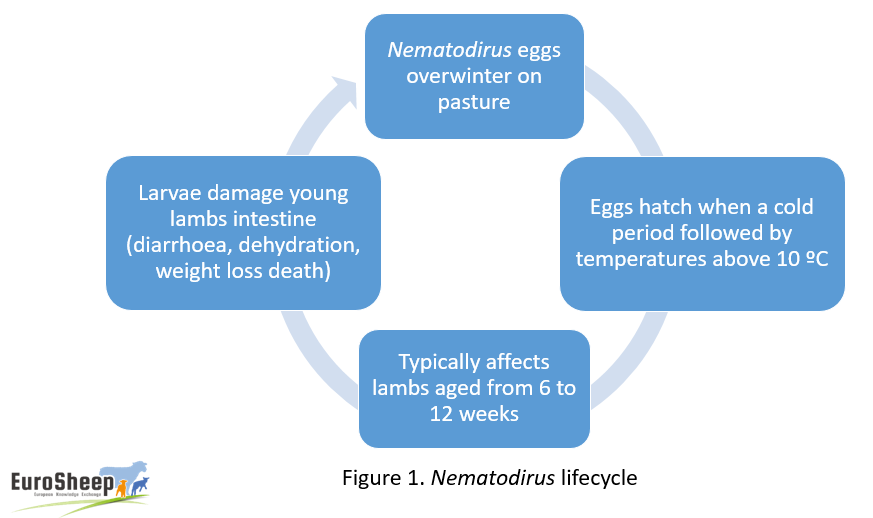
- Nematodirus battus is a parasite which typically affects lambs aged from 6 to 12 weeks but can occur in younger lambs.
- Nematodirus eggs overwinter on pasture from the previous grazing season and hatch when they are exposed to a cold period followed by an increase in temperatures above 10 ºC.
- In Ireland, this typically occurs from mid-April to May depending on location and conditions. The hatch coincides with the time when young lambs start consuming larger quantities of grass.
- The mass hatch poses a high level of challenge for young lambs.
- Once ingested the Nematodirus larvae damage the lining of the intestine resulting in diarrhoea, dehydration, weight loss and if left untreated can result in death.
- Sheep farms that are highly stocked are considered higher risk compared to mixed grazing systems on lower stocked farms.
Topic: Health
Production: Dairy / Meat
Animal Category: Adult / Lamb / Replacement
Issue: Internal Parasites
Level of Solution: Knowledge, Practical
Country: Ireland
How to implement it
- The Department of Agriculture, Food and Marine (DAFM) issues a Nematodirus forecast annually indicating when the hatch is likely to occur in different regions in Ireland.
- Use the DAFM forecast in combination with clinical signs and farm risk assessment to determine the best time to treat for Nematodirus.
- Clinical signs include diarrhoea, dehydration and wasting. However, as lambs may stop eating the diarrhoea may only consist of slimy mucus. Dehydrated lambs may congregate around watering troughs.
- Nematodirus is treated using anthelmintic drenches.
- There is no known case of resistance to any of the anthelmintic classes for Nematodirus in Ireland.
- Lambs should only be treated with a Benzimidazole (1-BZ – white drench) based product to preserve the efficacy of other drenches for later in the season.
- No anthelmintic offers residual activity against Nematodirus so a second treatment may be necessary, particularly in cases of mixed age grazing groups.
Expected benefits
Correct timing of Nematodirus treatment will positively affect lamb performance whilst use of white drenches will help prevent anthelmintic resistance on farms.
Prerequisites and/or limits
Understanding of risk period for Nematodirus and differences in anthelmintic classes.






